Population health is a term that has been gaining traction in the healthcare industry over the past decade. It represents a comprehensive approach to health that aims to improve the health of entire populations through the prevention, promotion, and management of chronic conditions.
As healthcare systems around the world continue to grapple with rising costs and increasing demand for services, population health initiatives have emerged as an essential strategy to reduce healthcare costs while improving patient outcomes.
Defining Population Health
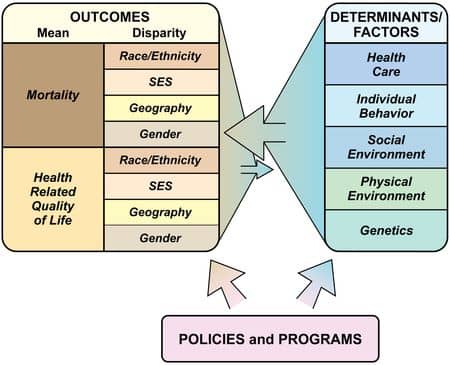
Population health is a comprehensive approach to healthcare that seeks to improve the overall health of an entire population by addressing determinants of health and managing chronic conditions.
Understanding The Concept Of Population Health
Population health is a relatively new concept that aims to take a broader approach to healthcare. It involves looking at the overall health status of a group of individuals, including their physical and social environments, genetics, medical care, behavior, and other factors that influence health outcomes. The goal of population health is to improve the overall health of communities by addressing these determinants.
One important aspect of population health is understanding how various factors contribute to positive or negative health outcomes within the group. By identifying these determinants and implementing interventions aimed at improving them, we can achieve positive health outcomes for entire populations rather than just focusing on individual patients. This interdisciplinary approach allows us to connect policy with practice and work towards better public health on a larger scale.
Overall, population health provides an opportunity for healthcare providers and local public health departments and-health authorities alike to focus on proactive strategies for improving community-based wellness. By encouraging healthy behaviors and reducing environmental hazards in areas prone to illness outbreaks or chronic diseases like diabetes or heart disease within groups most vulnerable (such as ethnic groups and disabled persons), population-level improvements are possible while achieving relative cost-effectiveness over time through evidence-based interventions designed for specific study populations based on eligibility criteria.
Key Components Of Population Health Management
Population health management involves several key components. One component is the collection of data about patient demographics and clinical history. This data provides a comprehensive picture of patients’ healthcare needs, enabling healthcare providers to develop targeted interventions to improve outcomes.
Another critical component is care coordination. In population health management, care teams work together to provide seamless transitions between different levels of care across multiple settings. This teamwork helps ensure that patients receive the right level of care at the right time from the appropriate provider.
Involving patients in their own care is essential for successful population health management. By engaging and empowering patients through education and shared decision-making, healthcare providers can help them achieve improved outcomes while reducing costs associated with preventable hospitalizations or emergency department visits.
Importance Of Population Health In Healthcare
Population health is becoming increasingly important in healthcare due to its potential to improve the overall health outcomes of a defined group of individuals. By taking a proactive approach, population health initiatives can prevent illnesses and diseases before they occur, ultimately reducing healthcare costs. Additionally, focusing on the determinants of health within populations allows for more effective interventions that can lead to improved quality of care and patient satisfaction.
The incorporation of a population health perspective into healthcare also prioritizes equity and coordination of care across diverse patient populations. With an emphasis on prevention and early intervention, those who are at risk or underserved can receive necessary care and ultimately achieve positive health outcomes. As healthcare systems move towards value-based care models, population health strategies will be crucial in improving both clinical outcomes and financial sustainability.
As medical staff continue to explore ways to improve the health status of patients while managing costs effectively, population health management should remain a core component of their strategy.
The Impact Of Population Health On Individual Health Outcomes & Healthcare Costs
Population health has a significant impact on individual health outcomes and healthcare costs. The concept of population health management involves improving the overall health status of a defined group, which can lead to better outcomes for individuals within that group. This approach has been shown to reduce healthcare costs by preventing unnecessary hospitalizations and emergency department visits.
Inadequate access to preventive services and chronic disease management can result in poor health outcomes for individuals, as well as increased healthcare costs. By focusing on population health, healthcare systems can address these issues at a broader level, ultimately leading to improved overall health outcomes and reduced costs. Additionally, promoting healthy behaviors among populations through community-wide interventions can lead to long-term improvements in individual health.
Benefits Of Population Health
Population health initiatives have numerous benefits, including the prevention of illness and disease, improved quality of care and patient satisfaction, enhanced health equity, and cost savings for healthcare systems.
Prevention Of Illness & Disease
Prevention of illness and disease is one of the primary objectives of population health management. By identifying risks and developing effective interventions to mitigate them, we can effectively limit the spread and incidence rates of common diseases. Through well-designed public health programs that include preventive measures such as vaccines, regular screenings, and access to appropriate medical care, communities can avoid costly infections.
Additionally, addressing social determinants like poverty, education levels or inadequate housing conditions can also help prevent illnesses from taking hold in a given community. For example, implementing policies that advocate for improved living standards in low-income neighborhoods might help reduce asthma symptoms caused by poor air quality. Moreover, investing in innovative technologies will aid us in promoting healthy lifestyles by leveraging big data sources concerning user activity levels or dietary choices, thus improving lifestyle choices for better patient outcomes.
Promoting prevention through population health is not only cost-effective, but it seeks to improve the overall quality of life for patients while achieving positive healthcare outcomes over time. By taking a holistic approach towards treating individuals within their respective communities through collaborative partnerships with local government entities and advocacy groups – providers are making major strides towards reducing preventable illnesses whilst improving the physical environment needed for better-individualized care service delivery across all groups in targeted populations at-risk such as ethnic minorities or those living with disabilities.
Improved Quality Of Care & Patient Satisfaction
One of the benefits of population health is improved quality of care and patient satisfaction. With a focus on prevention, providers can deliver more personalized and effective care to their patients. Providers who have access to electronic health information about their entire patient population can analyze data to identify trends, patterns, and risk factors that inform better diagnoses and treatment strategies which ultimately improve clinical outcomes.
Patient satisfaction is another critical aspect of healthcare delivery. Patient satisfaction correlates positively with the overall quality of health care services they receive from providers. Through initiatives like outreach programs or telemedicine interventions, healthcare systems are able to integrate convenient services into their offerings, catering for patients’ needs and increasing patient satisfaction. Improved communication through various channels also enhances coordination between patients and providers.
Enhanced Health Equity & Coordination Of Care
One of the main benefits of population health is the promotion of health equity and improved coordination of care. By focusing on the entire population, healthcare providers can identify gaps in access to care, such as socioeconomic or geographic barriers. Addressing these disparities can lead to better health outcomes for underserved communities and reduce overall healthcare costs.
With a population health approach, there is an increased emphasis on preventative care and early intervention, which can improve health outcomes for everyone. This includes identifying patients who are at risk for chronic conditions and implementing interventions that are tailored to their individual needs. Coordinated care between multiple providers also ensures that patients receive comprehensive, high-quality care that meets their unique needs.
Cost Savings For Healthcare Systems
One of the significant benefits of population health is its ability to save healthcare systems significant amounts of money. By focusing on prevention and early intervention, population health strategies can help reduce the number and severity of chronic diseases, which can be incredibly costly to treat. According to a report from the Milken Institute, The total estimated cost of obesity was 5.57 percent of GDP in 2014 and 9.3 percent in 2018.
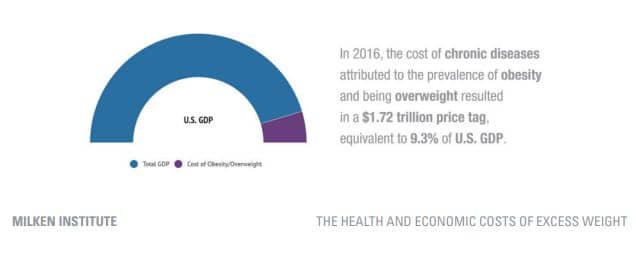
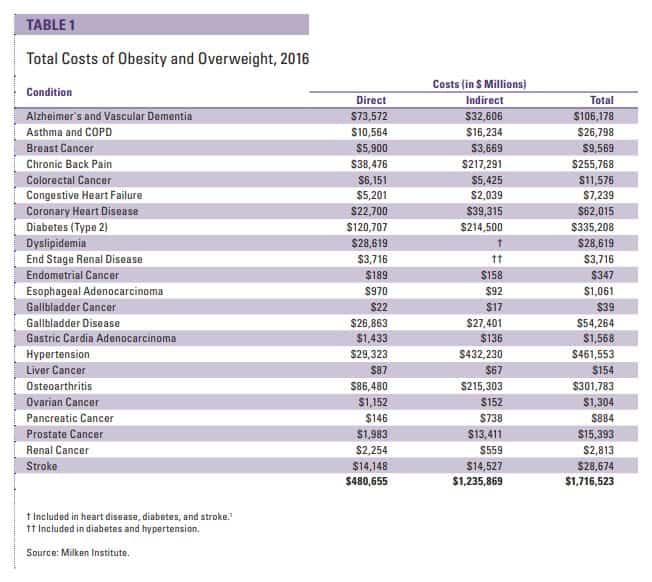
“The total cost of chronic diseases due to obesity and overweight [in 2018] was $1.72 trillion”
Additionally, by moving care closer to patients through telemedicine and community-based programs, healthcare providers can reduce costs associated with unnecessary hospital stays and emergency room visits. This has become increasingly important during the COVID-19 pandemic as many people are hesitant or unable to seek care in traditional settings.
Limitations Of Population Health
Limited Focus On Individualized Care
One limitation of population health is its limited focus on individualized care. While population health management aims to improve the overall health outcomes of a group, this approach may not address the unique needs and circumstances of each patient. This can be particularly challenging for patients with complex medical conditions or those who require specialized care.
Furthermore, focusing solely on population-level interventions can result in missed opportunities to address the specific health concerns of certain groups or individuals. Without considering personal preferences and experiences, healthcare providers may struggle to provide tailored treatment plans that effectively meet their patients’ needs.
Despite these limitations, incorporating individualized components into population health strategies can help achieve more positive health outcomes for patients as a whole. By embracing patient-centered models and taking into account social determinants of health, healthcare providers can deliver personalized interventions that are both effective and equitable.
Challenges With Access To Technology & Resources

Access to technology and resources is a significant challenge in population health management, particularly for rural communities. These barriers can limit the effectiveness of interventions targeting specific populations. Rural areas face particular challenges in accessing healthcare due to workforce shortages and transportation issues, which can impact their ability to receive timely care.
One solution that has emerged is the use of virtual healthcare, such as telemedicine and remote monitoring systems. These technologies have demonstrated promising results in improving access to care, especially for those living in remote locations or with limited mobility. However, using virtual healthcare requires a significant change in care models and ways of working within healthcare systems.
Despite advances made possible by new technologies, some groups still experience difficulties accessing necessary resources due to economic factors like poverty or lack of insurance coverage. This limitation highlights how social determinants of health play an important role in population health outcomes beyond traditional medical interventions.
Limited Understanding Of Social Determinants Of Health
Despite the notable benefits of population health, a limited understanding of social determinants of health is one limitation associated with this approach. Social determinants are non-medical factors that impact health outcomes and include conditions in which people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age. These determinants encompass a range of challenges that can directly or indirectly create barriers to improved health outcomes.
Examples of social determinants include safe and secure housing; English language proficiency and cultural understanding; access to education; transportation access; income levels; race/ethnicity; and health literacy levels. It’s been documented that these factors impact an individual’s ability to access healthcare services and meet their basic needs – ultimately impacting overall health status. Addressing these limitations within population health management requires addressing root socio-economic issues through partnerships with community-based organizations for prevention interventions targeting priority populations – including low-income households with chronic diseases like hypertension or diabetes mellitus type 2.
Limited Consideration Of Cultural & Linguistic Diversity
One of the challenges in population health management is the limited consideration of cultural and linguistic diversity. This can lead to inadequate healthcare access for individuals who do not speak or understand the local language or have cultural practices that differ from mainstream society. Such barriers to care can result in worse health outcomes, including delayed diagnoses and increased hospitalizations.
To address this limitation, it is essential for healthcare providers and systems to consider cultural competency training as part of their population health strategies. Training on diverse cultures, languages, and beliefs helps providers understand patients’ backgrounds better and tailor treatment plans accordingly. Additionally, utilizing interpretation services or offering multilingual resources can increase access to care for non-English speakers, improving overall health outcomes within diverse communities.
Strategies For Population Health Management
To effectively manage population health, strategies such as collaborative partnerships, leveraging technology and data analytics, patient-centered care delivery models, and evidence-based interventions are crucial. Read on to learn more about successful population health initiatives and the challenges involved in implementing them.
Collaborative Partnerships & Community Involvement
Collaborative partnerships and community involvement are crucial for achieving positive population health outcomes. By working together, healthcare providers and community organizations can identify effective interventions and address complex health issues. Multisector partnerships across multiple sectors of society are necessary for population health improvement.
Community involvement is essential for identifying the needs of the population and implementing targeted solutions. Collaborations with broad population health goals, such as preventing disease and reducing health inequalities, have a positive impact on overall health outcomes. Community health partnerships that bring clinicians together with civic groups, social service providers, and educational leaders can improve various determinants of health, including physical environment, social environment, economic stability, etc., which ultimately contribute to improved public/human/global/individual/community’s overall health status.
Leveraging Technology & Data Analytics
Leveraging technology and data analytics are integral components of successful population health management. Data analytics tools can assist in identifying patient populations most at risk, predicting outcomes, and developing targeted interventions. This approach ultimately leads to improved care coordination and patient outcomes.
In today’s digital age, sophisticated projects integrate diverse datasets from electronic medical records (EMRs), social determinants of health (SDH) sources, survey results, public health information systems (PHIS), and environmental data to support population-level efforts. This amalgamation helps healthcare organizations better understand the needs of their communities while also streamlining operational efficiency.
Utilizing technology allows for more efficient communication among providers across settings such as telemedicine platforms or patient portals. Patients benefit from increased access to their healthcare providers through secure online messaging or virtual visits that reduce the need to make time-consuming appointments with a practitioner.
Patient-Centered Care Delivery Models
Patient-centered care delivery models are essential to achieving positive health outcomes for individuals. This approach focuses on the needs and preferences of each patient, allowing healthcare providers to customize their treatments accordingly. Patient-centered care goes beyond just medical treatment; it takes into account the social determinants of health, addressing factors such as housing, education, and employment that can impact overall health.
The patient-centered medical home (PCMH) model is one effective method for delivering primary care in a patient-centered way. PCMHs provide comprehensive care that includes chronic disease management, preventive services, and coordination with specialty care providers. Research has shown that PCMHs can improve quality of care while also reducing costs by avoiding unnecessary hospitalizations and emergency department visits.
Collaborative practice models such as interprofessional practice and team-based care are another strategy for putting patients at the center of their own healthcare. These models involve a variety of healthcare professionals working together towards common goals such as improving outcomes or managing chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension. With support from these collaborative teams, patients can take more control over their own health and better manage their conditions alongside their medical providers.
Examples Of Successful Population Health Management
Kaiser Permanente and Geisinger Health System are two notable examples of successful population health management initiatives, both of which have implemented innovative approaches to care delivery and patient engagement that have led to improved health outcomes and cost savings.
Kaiser Permanente
Kaiser Permanente is a leading example of successful population health management. This organization has developed a strategy to achieve better health outcomes for its patients by tracking population health trends and implementing proactive primary care and patient-panel management. Kaiser Permanente’s integrated care model allows access to data across large numbers of patients over long periods, facilitating effective population health management.
In addition to tracking healthcare data, Kaiser Permanente’s population health strategies consider social determinants of health, including socioeconomic factors that play a significant role in individualized healthcare. The organization’s approach demonstrates how considering multiple determinants of clinical outcomes can produce overall improvements in the community’s physical environment and public health initiatives.
Overall, Kaiser Permanente is an essential example for understanding the potential impact of managing the well-being of defined groups on clinical outcomes and other aggregate measures such as relative cost-effectiveness- known as Triple Aim Approach. As such, Kaiser has been recognized for exercising key models towards quality achievement through case studies by Commonwealth Fund and Exercise is Medicine  which have led to improved healthcare improvements among employees, ethnic groups disabled persons among others sustaining collaboratives with local government entities for broader implementation success stories.
which have led to improved healthcare improvements among employees, ethnic groups disabled persons among others sustaining collaboratives with local government entities for broader implementation success stories.
Geisinger Health System
Geisinger Health System is an integrated health system that serves over 3 million people in rural northeastern and central Pennsylvania. As a physician-led nonprofit organization, Geisinger has paved the way for successful population health management by optimizing patient outcomes while advocating for valuable healthcare services. Their ProvenCare® program uses evidence-based protocols for specific medical procedures like coronary artery bypass surgery, resulting in better outcomes for patients at lower costs to the system.
To address disparate health outcomes and provide quality care to their patients, Geisinger uses electronic health records (EHRs) linked to contextual data using geographic information systems (GIS). This approach enables precise and effective management of population-based needs while addressing underlying social determinants of health.
One significant advantage of a provider-sponsored health plan like Geisinger’s is greater accountability and responsibility over members’ overall well-being across an extended period. Through this model, Geisinger can prioritize preventive measures that reduce costs without sacrificing high-quality medical care—ultimately improving both individual patient satisfaction and community-wide health outcomes.
Challenges To Implementing Population Health
Implementing population health initiatives can be challenging due to financial incentives and reimbursement models, health equity concerns, regulatory barriers, and resistance to change, as well as limited interoperability and data sharing.
Financial Incentives & Reimbursement Models
One of the biggest challenges to implementing population health initiatives is finding sustainable financial incentives and reimbursement models for healthcare providers. Traditional fee-for-service payment models do not align with the goals of population health management, which focuses on preventative care and improving health outcomes across a whole community rather than just treating individual patients. Pay-for-performance initiatives, bundled-payment models, and capitation have all been proposed as alternatives to incentivize healthcare providers to focus on providing high-value care that produces better patient outcomes while reducing costs.
Pay-for-performance programs can improve clinical outcomes while increasing provider compliance with best practices. However, there are concerns about potential unintended consequences such as risk aversion among providers or gaming the system by focusing only on metrics that are being measured. Bundled payments offer an alternative approach where providers are paid a set amount for all services related to a particular condition or episode of care, regardless of the number or complexity of services required. This model may be particularly effective in encouraging collaboration between different specialties and reducing unnecessary interventions.
Health Equity Concerns
One of the most significant challenges associated with implementing population health is addressing issues of health equity. Health equity refers to ensuring that everyone has equal access to healthcare and the opportunity to attain their highest level of health. However, many factors, such as social determinants, economic status, and limited access to healthcare, can impede efforts toward achieving this goal.
Health disparities and inequities are systematic differences in health outcomes between different groups of people that can impact overall population health. These disparities often affect vulnerable populations like ethnic minorities, low-income individuals, and disabled persons more acutely than other groups. Addressing these disparities is critical for improving overall population health outcomes.
Regulatory Barriers
One of the significant challenges to implementing population health strategies is regulatory barriers and resistance to change within healthcare systems. Healthcare regulations are often complex, with a variety of federal, state, and local regulations that can be difficult to navigate. This complexity makes it challenging for healthcare organizations to implement new models of care delivery or payment structures.
Limited Interoperability & Data Sharing
One of the main challenges in implementing population health is limited interoperability and data sharing among healthcare systems. Legacy health IT systems often struggle to collect, store, and share race, ethnicity, and language data needed for effective population health management.
Interoperability issues also impact the exchange of clinical information, which is crucial for coordinated care delivery within and across healthcare organizations. Patient data must be shared effectively to enable providers to collaborate effectively on treatment plans; however, this can prove difficult when using incompatible technology or accessing fragmented sets of medical records.
Efforts are underway to establish a nationwide interoperability roadmap that would support better coordination among stakeholders in achieving population health goals. This includes improving data collection methods across healthcare systems as well as developing new policies around secure yet comprehensive health data exchange that can improve care coordination while reducing hospital readmissions and saving hospitals money.
Conclusion
Population health is a vital approach to improving the overall health of communities by addressing the determinants of health and proactively managing specific health concerns. By leveraging technology, data analytics, and community involvement, population health programs can achieve positive outcomes within different populations and settings. For more information about successful strategies in population health management and overcoming challenges to implementation, continue reading this blog post.
As the healthcare industry advances, we can expect population health to be integrated with the latest technological innovations. These include new treatments, devices, and social media platforms that can help promote healthy behavior and monitor patient progress remotely. We can also expect a greater focus on addressing social determinants of health (SDOH) as an essential component of population health management.
Further Reading
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1447747/
https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-019-7002-z
https://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2016/15_0565.htm
https://wa.kaiserpermanente.org/static/pdf/public/about/population-health-2020.pdf
https://onlinepublichealth.gwu.edu/resources/what-is-population-health/
https://milkeninstitute.org/sites/default/files/reports-pdf/ChronicDiseases-HighRes-FINAL.pdf
https://milkeninstitute.org/sites/default/files/reports-pdf/Next-Gen-Prevention-GSG-FINAL2_0.pdf




